
Airglow is explained in detail in this ESOcast. The beautiful red and green colours in the sky are due to atmospheric airglow, another light-related optical phenomenon. This is occurring in this unusual image, where a rare corona of the planet Jupiter can be seen above the Atacama Desert in Chile. However, there is also the optical phenomenon of a corona, caused by the diffraction of light from a bright object - such as the Sun, other stars, the Moon, and bright planets - by water drops or ice crystals in the Earth’s atmosphere. An image of the Sun’s corona as seen during a 1999 eclipse can be seen here. The solar corona then appears as a bright ring surrounding the eclipsed Sun. For the Sun, we can best see this corona during a solar eclipse, when the Moon passes in front of the Sun and covers our star’s face. (See Template:PD-USGov, NASA copyright policy page or JPL Image Use Policy.Stars are surrounded by something known as a corona - a diffuse aura of plasma that appears to surround them in the sky. NASA copyright policy states that "NASA material is not protected by copyright unless noted". This file is in the public domain in the United States because it was solely created by NASA. This image was originally posted to Flickr by NASA Goddard Photo and Video at It was reviewed on 17 September 2016 by FlickreviewR and was confirmed to be licensed under the terms of the cc-by-2.0.ġ7 September 2016 Public domain Public domain false false CC BY 2.0 Creative Commons Attribution 2.0 true true You may do so in any reasonable manner, but not in any way that suggests the licensor endorses you or your use. attribution – You must give appropriate credit, provide a link to the license, and indicate if changes were made.to share – to copy, distribute and transmit the work.NASA Goddard Space Flight Center from Greenbelt, MD, USA Two Coronal Holes on the Sun Viewed by SDO Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. NASA Goddard Space Flight Center enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. The bright active region on the lower right quadrant is the same region that produced solar flares last week. Magnetic fields that loop up and back down to the surface can be seen as arcs in non-coronal hole regions of the image, including over the lower right horizon. The magnetic field in these regions extends far out into space rather than quickly looping back into the sun’s surface.

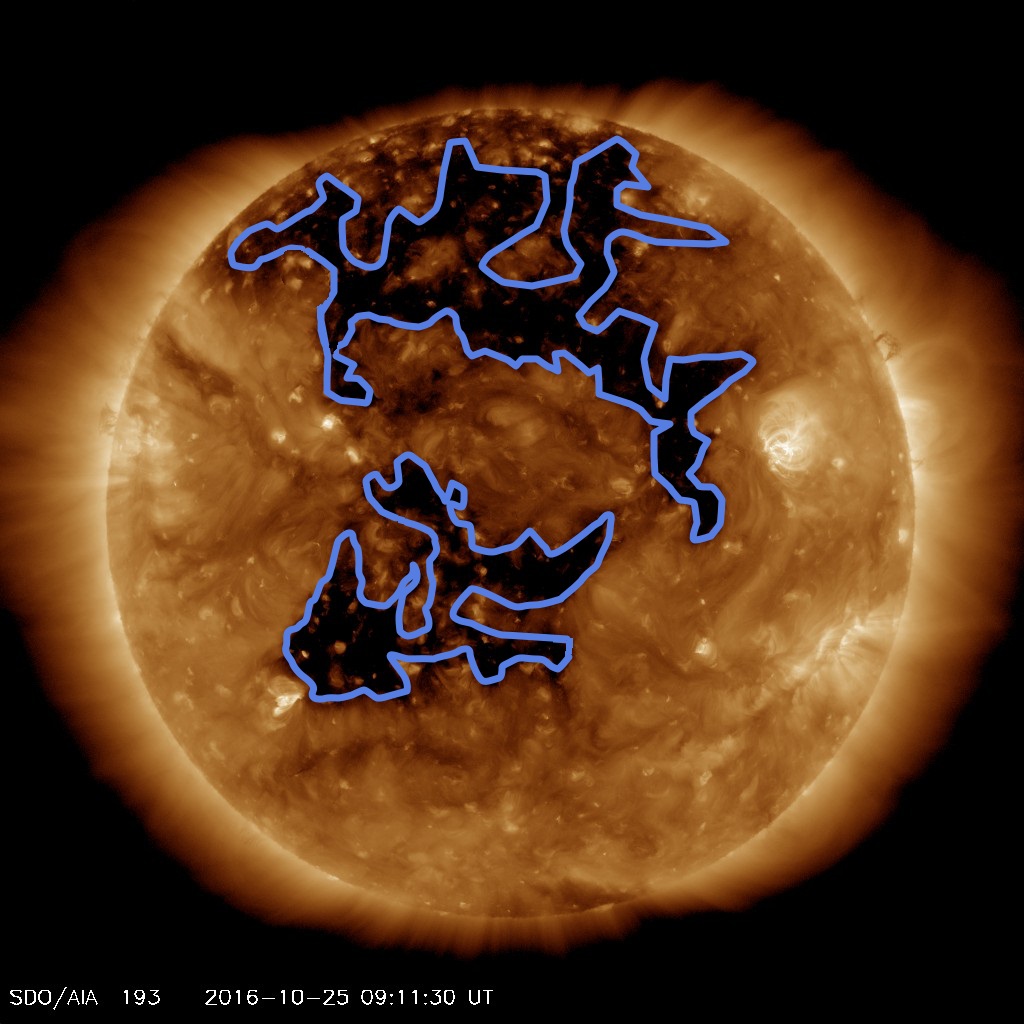
Coronal holes can be a source of fast solar wind of solar particles that envelop the Earth. It covers about 3.8 billion square miles on the sun - only about 0.16-percent of the solar surface.Ĭoronal holes are lower density and temperature regions of the sun’s outer atmosphere, known as the corona.
#SUN CORONA HOLE 2016 PLUS#
Rodmann J (2016) The wide-field imager for solar probe plus (WISPR). The smaller coronal hole, towards the opposite pole, is long and narrow. Hayashi K, Hakamada K (2017) Relation between coronal hole areas and solar wind. While that may not sound significant, it is one of the largest polar holes scientists have observed in decades. The larger coronal hole of the two, near the southern pole, covers an estimated 6- to 8-percent of the total solar surface. English: NASA’s Solar Dynamics Observatory, or SDO, captured this solar image on March 16, 2015, which clearly shows two dark patches, known as coronal holes.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
